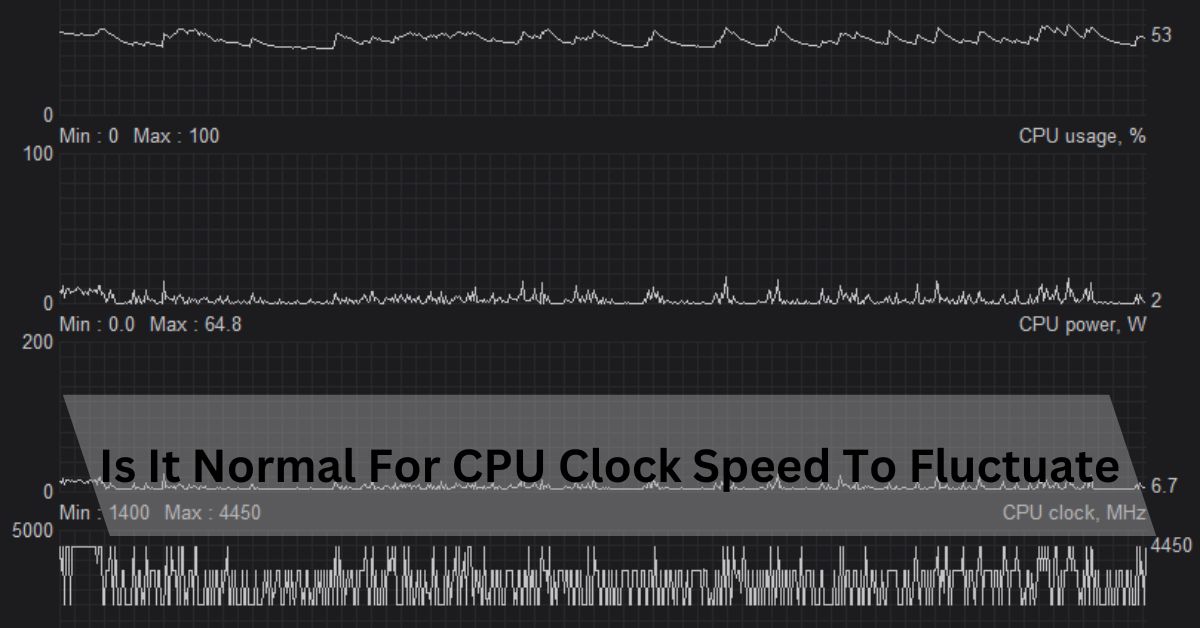
While talking about the focal handling unit (central processor), your PC’s heart, the expression “clock speed” often comes up. In any case, if you’ve checked your machine’s showcase at any point, you could have seen that the clock speed isn’t persistently unsurprising—it changes.
Yes, it’s not unusual for CPU clock speeds to vary. Modern CPU’s are designed to alter their clock speeds dynamically based on contemporary workloads and thermal situations.
This article will investigate why these fluctuations arise and what they imply to your laptop.
Understanding CPU Clock Speed:
Before delving into the reasons behind clock velocity fluctuations, it’s crucial to apprehend what clock pace is. The CPU clock pace refers to the price at which a CPU can complete a processing cycle. A better clock pace commonly results in a quicker CPU that can manage greater responsibilities concurrently. However, this isn’t the sole determinant of overall performance, as architecture, cache length, and different elements additionally play giant roles.
Also Read: How To Know If A Graphics Card Is Good?-Complete Guide
Reasons for Clock Speed Fluctuations:
Several factors can cause your CPU clock pace to vary. Here are the most not unusual ones:
1. Dynamic Voltage and Frequency Scaling:
When the machine demands extra overall performance, the clock speed will increase. Conversely, when the demand is low, the clock velocity decreases to shop strength and reduces warmth output.
2. Thermal Throttling:
CPU’s generate heat, and excessive heat can damage the processor. CPU’s are equipped with thermal throttling mechanisms. When the temperature reaches a crucial threshold, the CPU routinely reduces its clock velocity to calm down. That is a defensive measure to ensure the longevity and stability of your hardware.
3. Power Limits and Turbo Boost:
Many CPU’s, especially those from Intel and AMD, have a function called Turbo Boost (Intel) or Precision Boost (AMD). That permits the CPU to briefly increase its clock velocity beyond the base frequency to address annoying duties. However, this enhancement is restrained by electricity and thermal constraints. When those limits are reached, the CPU clock pace will lower to preserve safe operating situations.
4. Background Processes:
Your computer runs numerous legacy procedures even when you’re not actively using it. These processes can cause minor fluctuations in CPU clock velocity because the gadget dynamically adjusts to address these obligations efficiently.
Impact on Performance:
The fluctuations in CPU clock pace are usually not something to worry about. Here’s why:
1. Optimized Power Consumption:
By adjusting the clock velocity in step with the workload, your CPU ensures that it uses energy efficiently. That now not only reduces your energy payments but also contributes to the durability of your system by minimizing heat generation.
2. Performance on Demand:
The potential to boost clock pace dynamically means that your CPU can offer extra overall performance whilst needed. For instance, whilst going for walks, a heavy application, or sports, the CPU can ramp up its speed to ensure easy overall performance. Once the undertaking is completed, it’ll return to a lower pace to save electricity.
3. System Stability:
Thermal throttling is a safeguard designed to shield your CPU from harm. While it can cause transient performance drops, it prevents overheating, ensuring that your machine stays solid and practical over the long term.
Also Read: Can A Motherboard Bottleneck A GPU?-Complete Guide
Monitoring and Managing Clock Speed:

While clock speed fluctuations are ordinary, monitoring your CPU to ensure everything is functioning is fantastic. Here are a few equipment and suggestions for monitoring and dealing with your CPU clock pace:
1. Monitoring Tools:
- HWMonitor: This tool provides detailed statistics about your device’s hardware, including CPU temperature and clock pace.
- CPU-Z: A lightweight device that offers actual-time monitoring of your CPU’s clock speed, voltage, and other vital parameters.
- Task Manager: For Windows users, the built-in Task Manager (below the Performance tab) can provide a basic overview of their CPU utilization and speed.
2. Cooling Solutions:
Ensuring that your CPU has good enough cooling is essential. That can involve cleaning dirt from your system, using exquisite thermal paste, or investing in better cooling solutions like larger heatsinks or liquid cooling structures.
3. BIOS/UEFI Settings:
Many motherboards permit you to tweak CPU settings through the BIOS/UEFI interface. You can limit the maximum clock speed or regulate electricity settings to discover a balance between overall performance and temperature.
4. Software Management:
Some operating systems and software program utilities provide strength control profiles. For instance, Windows has power plans that you could modify to balance overall performance and strength intake. Choosing a “Balanced” or “Power Saver” plan can help you correctly manipulate clock pace fluctuations.
When to Be Concerned:
While clock velocity fluctuations usually are ordinary, there are a few scenarios that you may need to analyze in addition:
1. Consistent Throttling Under Light Load:
If your CPU is throttling regularly, even below mild or slight loads, it indicates overheating trouble or a malfunctioning cooling machine. Check your CPU temperatures and make sure your cooling solutions are running efficiently.
2. Unusual Performance Drops:
Observing large performance drops for the duration of recurring tasks could signal thermal issues, electricity delivery issues, or even malware. Running a full gadget scan and checking for historical past strategies may assist in discovering the motive.
3. High Idle Temperatures:
High temperatures when your machine is idle can indicate harmful cooling or dust buildup in your PC case. Regular upkeep and cleansing can help alleviate this.
Also Read: CPU Ratio Offset When Running AVX?-A Complete Guide
FAQ’s:
1. Is CPU clock speed consistent?
The clock frequency of a CPU can range due to several elements, and it is not constantly consistent.
2. Is CPU pace alleged to alternate?
CPU’s only run at their full pace once they want to, so there isn’t plenty of load on the CPU.
3. What is an everyday clock speed for the CPU?
Modern processors usually have speeds between 1 GHz (gigahertz) and 3. 8 GHz, with higher-give-up fashions able to achieve even higher speeds.
4. How do I fix CPU velocity drop?
Usually, an unexpected drop in CPU speed indicates an overheating problem. Try to smooth your PC fans and air vents: it typically helps.
Conclusion:
In precision, it’s miles regular for CPU clock pace to range. Modern CPU’s are designed to adjust their speeds dynamically to stability performance, strength intake, and thermal control. These fluctuations ensure that your system runs successfully and stays stable over time.
By understanding the motives behind these fluctuations and tracking your machine’s performance, you can ensure that your CPU operates optimally and avoids potential troubles. Remember, occasional dips in clock pace are a part of your CPU’s sensible design, preserving your computer jogging efficiently and correctly.